The quality of internet connection plays a significant role in making your live streaming successful. However, many other factors need some consideration. Some of our clients often ask us how much traffic will be there when live streaming for one hour? Also, how long does it take for one 6 or 128G storage TF card recoding?
So, let's find out the best way to calculate the 4 G traffic during live streaming.
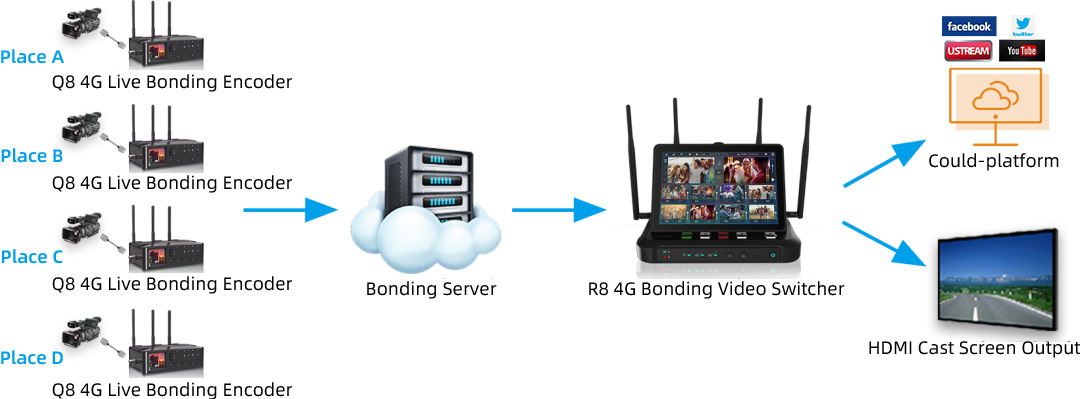
The typical topology of live broadcast figure diagram
Four Parts Involved in the Traffic
Before we go ahead, it is necessary to understand the concept of traffic in detail. When we think about the traffic, we must also consider the four parts involved in it. These parts are:
1. The first part is user's SIM card traffic. It also means the upstream bandwidth traffic required by the encoder to push streaming.
2. The second part is bonding server traffic. It doesn't involve single card push streaming or open aggregation.
3. The third part is the Cloud platform redistribution traffic.
4. Lastly, the fourth part is the Downstream traffic. It is basically viewed by clients using a mobile, computer, and other devices (same as watching video sites.)
We will further elaborate these four parts in the following section of this post. Before that, let's understand the two more important factors.
Bandwidth and Bit Rate
Internet users often use two popular terms to refer to their internet speed. They are bandwidth and bit rate.
1. Bandwidth:
The first term is the network speed, i.e. the bandwidth. Its unit is bps. In short, it determines the number of bits transmitted per second. For example, if you install a 100-megabit broadband connection in the home, then it means that you will get a speed of 100-MBPS.
2. Bit Rate
The second significant term is the bit rate, i.e. the traffic. Its unit is bytes (B). For example, we receive 5GB or 10GB per month with a mobile phone package. It is necessary to understand the difference between b and B. Remember, 1 Byte equals 8 bits. We can use this value during the bandwidth conversion traffic within a specific timeframe.
Factors Involved in Traffic Calculation
As said earlier, we will now focus on four crucial factors that are involved in the calculation of cellular traffic.
1. User's SIM Card Traffic
The general formula is - (bit rate) x (time) ÷ 8bit. For example, if you set the live broadcast bit rate to 1Mbps, then the calculation formula for the traffic consumed per hour will be 1Mbps x 3600 seconds (1 hour) ÷ 8bit = 450MB. Similarly, if the live broadcast bit rate is 2Mbps, then the hourly traffic is 2Mbps x 3600 seconds (1 Hour) ÷ 8bit = 900MB. So, the traffic fees involved in this part are the fees for users to purchase traffic cards themselves.
2. Bonding Server Traffic
In this part, we will calculate the bonding server traffic. This calculation method is the same as the user's SIM card traffic. As much as the push traffic device pushes up, the aggregation server accepts as much traffic as possible. After that, it sends it to the cloud platform after correcting the error. For example, if the aggregation service is deployed in Alibaba Cloud, then Alibaba Cloud will charge this part of the traffic fee.
3. Cloud Platform Redistribution Traffic
If the live streaming bit rate set by the streaming device is 2Mpbs, then the bandwidth of direct streaming or streaming to the cloud platform through the aggregation server will also be 2Mpbs.
Well, it is the upstream traffic to the cloud platform. So, the upstream traffic is fixed in most cases. However, in the case of downstream traffic, it depends on the number of users watching the live streaming.
Besides, if the cloud platform does not make transcoding rate reduction, then each viewing user will consume a piece of traffic. So, if each user views for an hour, then each user will consume the cloud platform’s traffic, which is 900MB.
Of course, in addition to traffic, the cloud platform also involves bandwidth issues. If N users are watching at the same time, then the bandwidth is N x 2Mpbs.
4. View Traffic
Users can use either Wi-Fi traffic or traffic to view live streaming. Here also, the traffic calculation method is the same as that of the user's SIM card.
Now, the main question may come to your mind - how to calculate the recording storage space. Well, you can use the same formula as that of the user's SIM card traffic calculation method. Firstly, you need to set your recording bit rate to 10Mbps. So, the storage space required per hour is 4.5GB. Also, for a 6 or 128G TF card, you will get the storable time by dividing the capacity with the hourly consumption.
Final Thoughts!
In this way, you can calculate the traffic during live streaming. You have to consider various factors to calculate the traffic.